Creating a sitemap is a very important point for the optimization of any website. Sitemaps, report the structure of your website to search engines and also include some metadata, such as:
- Specifies how often the pages are updated.
- It indicates when the pages last changed.
- Shows the importance level of pages which are linked off each other.
- Sitemaps also stand out in the following ways:
- Contains archived content that is not related to one another.
- It arranges external links.
- It can contain hundreds or even thousands of pages.
As the name implies, sitemaps allow search engine bots to find and discover the most important pages on your website.
Let’s move on how you can create a sitemap and optimize it.
1 – Tools and Plugins to Automatically Create a Sitemap
You can easily create a sitemap if you have any XML Sitemap creation tool or if you are using a tool such as Google XML Sitemaps .
Yoast SEO also one of the easy to use tool especially for WordPress. You can have a direct XML sitemap, by just choosing the Yoast SEO add-on.
As an alternative, you can manually create a sitemap by examining a sample code structure of an XML sitemap. Technically, all you need is; a text file that separates each URL from each other and writes to new lines. But if you want to implement an hreflang, you need a complete XML sitemap. To create a sensible sitemap, the best option will be to use a tool.
2 – Integrate Google with Your Site Map
You can use Google Search Console to promote your sitemap to Google. To do that follow Crawl – Sitemaps – Add Test Sitemap steps through the dashboard.
Click Submit Sitemap and check the results to see if there are any problems or see any of your mistakes. Ideally, the number of pages indexed should be the same as the number of pages you submitted.
When you introduce Google to your sitemap, Google will know which of your pages have higher quality and is worthy of indexing. But don’t forget that does not mean that the related pages will be indexed as a guarantee.
3 – Prioritize High-Quality Pages in Your Sitemap
In terms of ranking, the overall quality of your site is a very important factor for all search engines. If your sitemaps includes shoddy pages of your site, search engines will think your website is of poor quality and will decide not to visit or lower the crawl rate.
So for the search engine bots the most important pages of your site should be:
- Highly optimized pages
- The pages contains pictures and videos.
- Pages with unique content.
- High user interaction pages.
4- Ignore Your Untagged Pages
The most annoying thing about indexing is, you will never know which pages will be indexed or not indexed. For example; If 20,000 pages were sent to a search engine and 15,000 of them were indexed, it would not be predicted in advance which 5,000 pages are found as problematic by the search engine. This is particularly very common in e-commerce websites which have similar products.
Google Search Console has recently released an update to avoid this problem. The problem pages are now listed so now after finding the problem pages, there is only one thing left to do: mark these pages as “noindex” . Thus, there will be no decrease in the overall site quality.
5 – Add Only Canonical Versions of Your Site Harness URLs
If you have pages with very similar products (like different colors of the same product), you can tell Google that you have a “main” page for these products. You need to use the “real = canonical” tag for this. If you need details about exactly what this tag is, you can have much more information on our article.
6 – Use Robots.txt wherever possible
Robots.txt is a text file created to explain to search engines, how to crawl pages of your website. When you do not want a page to be indexed, you should use meta-robots that use the “noindex, follow” tag on your Robot.txt file instead of a Sitemap. This will prevent related pages from being indexed by Google and protect your unique link.
This is also useful for side pages that you do not want to appear on search engine result pages. You may want to use a robots.txt file if you notice that Google has added indexes instead of your homepage pages.
You can read our blog post to find out more about exactly what the robots.txt file is.
7 – Do not add your “NoIndex” URLs to your SiteMaps
Adding a website inside sitemaps means that “This page is important, you absolutely must add it to the index” for search engines. But same time by adding “noindex” marked website in the same list means “I do not allow you to index this junk page.“. It is one of the mistakes should not be done, but also done by a lot of website owners. While creating a misleading operation for search engines also you are increasing your file size.
8 – Create Dynamic XML Sitemaps for Large Sites
It is impossible to track all the meta robots for large websites. So you should need to introduce some rules for your XML sitemap, and make sure that it does the relevant required operations instead of you. This may require some technical knowledge.
9 – Use RSS / Atom Feeds Next to XML Maps
When you update a page or when you add new content to a page RSS / Atom Feeds transfer them to search engines. We recommend you that use both Sitemaps and RSS / Atom feeds on your website. So that Google’s search bots know which pages should be crawled and indexed.
10 – Just Edit Modification Time When You Really Make Changes
If you have not made any significant changes to your page, do not try to trick search engines by updating your modification time. Some website owners to have a better ranking on Google or Search Engines they just edit modification time. Even it seems like working in a very short time, usually, this story ends with ignorance of your modification and your website with Google.
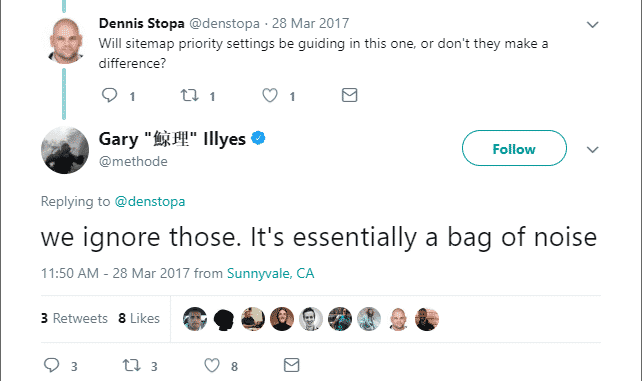
11 – Do Not Stick to Priority Settings
Some Sitemaps uses “Priority” columns to determine which pages are most important for search engines. For last years there are several discussions that it is useful or not, but last year Gary Ellis, who was on Google’s staff, put an endpoint in this discussion. He said that they ignore it. So while preparing sitemap you don’t need to determine any priority, especially for Google.
12 – Keep File Size Small as Possible
Until 2016, Google and Bing agreed that the maximum size of the sitemap file should be 10 MB. But in 2016 this rule changed to 50 MB.Even now it is 50 MB we recommend that, instead of using the full 50 MB keep your file size as small as possible. Because having smaller sitemap means you need to use less source of server and hosting.
13 – Use Multiple Sitemaps if Your Site exceeds 50,000 Pages
Sitemaps are limited 50,000 URLs per file. This limit is sufficient for most sites, but sites with more than 50,000 URLs must create multiple Sitemaps. Large eCommerce websites and portal websites are examples of this.


Leave A Comment?